Digigram has developed a solution to transport composite MPX signals from the studio over an IP network with the same quality and reliability as a point-to-point link.
MPX (multiplex) is the composite signal dedicated to the transmitter site. It is the only signal accepted by the transmitter (exciter) for FM diffusion, and it is traditionally delivered via a point-to-point link.
What are the main differences for an MPX signal delivery, between an IP wireless point-to point-link, and an IP network link?
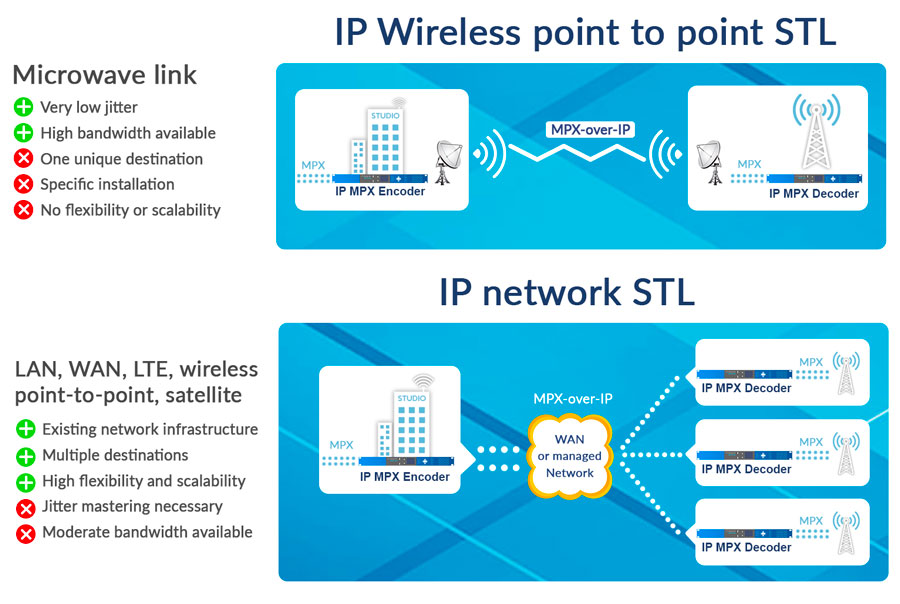
There are two distinct advantages of an MPX-over-IP transport solution for broadcasters:
The first is a significant gain in flexibility and scalability; and the second is a reduction in equipment to be maintained and deployed on the transmitter sites. However, to ensure the same levels of quality and reliability over an IP network as for a point-to-point link, attention needs to be paid to IP transport and jitter mastering.
IP mastering
Built on the universally acclaimed IQOYA audio-over-IP platform, Digigram has developed a highly reliable solution allowing broadcasters to deliver MPX signals over IP networks. All the mechanisms that have helped to make IQOYA a worldwide success for rock-solid audio-over-IP streaming have been deployed for MPX transport over IP. That includes FEC, dual streaming with time diversity, network jitter mastering, and smart synchronisation on the incoming stream. Plus, additional smart features have been added, such as decoder synchronisation for MFN, and auxiliary data tunnelling.
Jitter mastering
Why is it important to master the jitter? Mastering the jitter guarantees the same reliability as a point-to-point link. That means that transporting MPX signal can be achieved either via point-to-point or over an IP network depending on the broadcaster’s requirements.
Data rate mastering
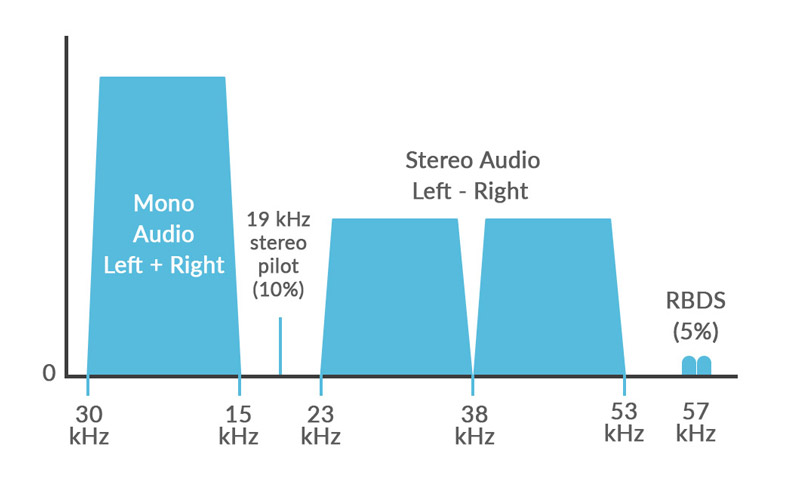
MPX is a composite signal, hence smart codec design requires far less dynamic range than baseband audio. For instance for Audio stereo + RDS, 144 kHz sample rate @12 bits encoding with analog transmission leads to a very acceptable 2 Mb/s instead of the usual 3.3 Mb/s or more. With AES192 digital MPX transport 2.6 Mb/s can in addition transport an auxiliary subcarrier.
Conclusion
The IQOYA hardware codec is a highly versatile codec for program delivery. It delivers analog or digital baseband audio or MPX through point-to-point or IP networks links. These baseband audio links are distributed to FM transmitter sites, web radio CDN, and/or DVB multiplexers for satellite, and DAB encoders for digital radio.
Digigram is proud to be one of the few in the world able to transport MPX over IP network with a very high jitter resilience and acceptable bandwidth.





